-S@
Four-Easy Pieces
Building off the work of mathematician Dr. Stephen Wolfram and his book “A New Kind of Science” (2002), an analytical key; a touch of Richard Feynman and a splash of Isaac Asimov to get a basic computer programming logic for embedded systems with just four-easy pieces.
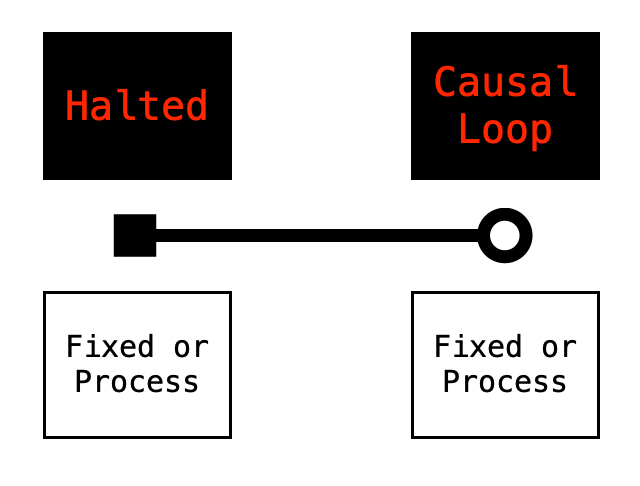
Halted and Casual Loops
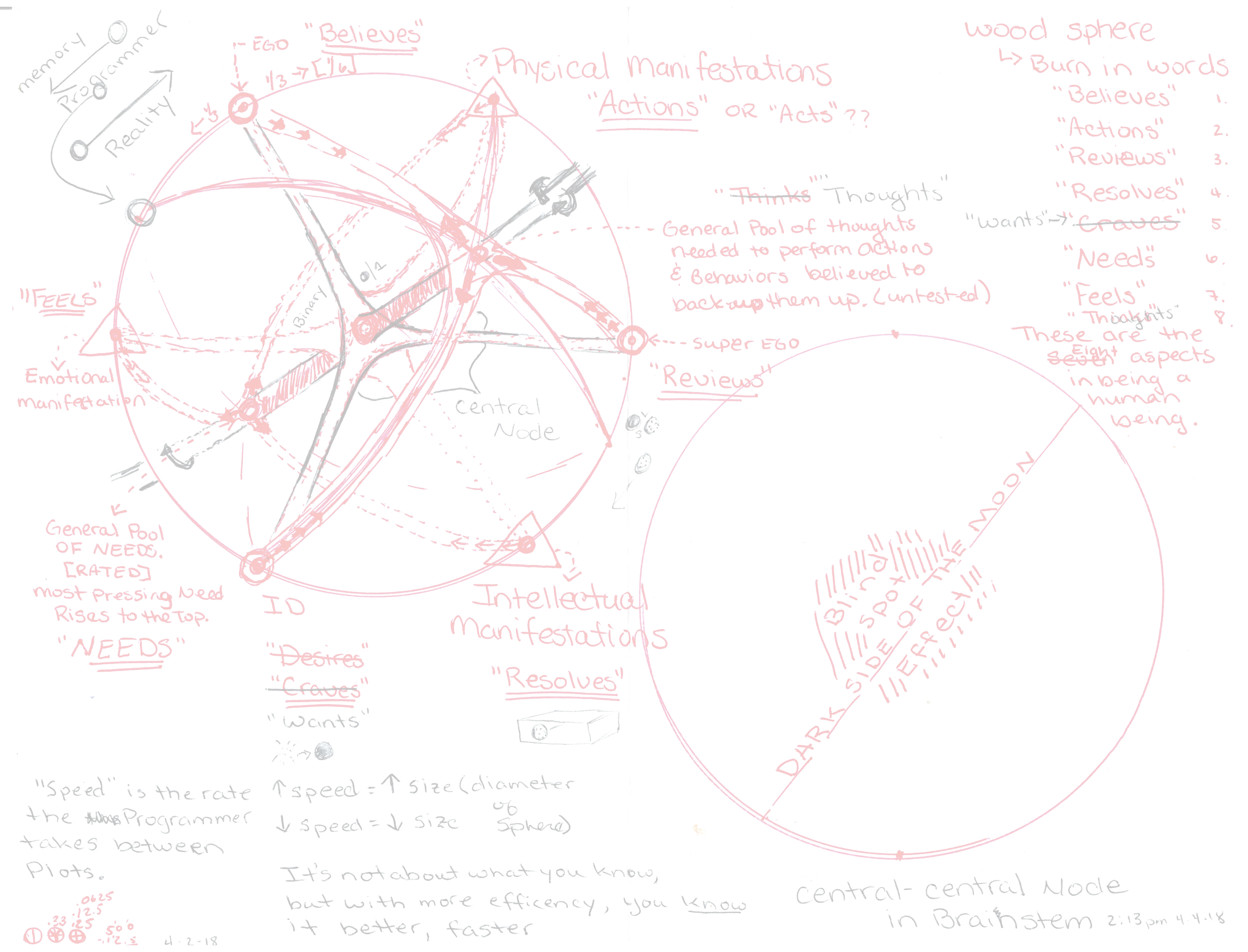
These top or major concepts never change and the endpoints of the line was selected to represent them. The bottom labels represent minor variations of the major concepts. These minor concepts alternate each time a sub-layer is established, regardless of it being labeled as Halted or Casual Loop.

Fixed and Process
This recombination of sub-labels allows for a type of logic-mixing to occur. This illustration starts with a zero-layer which for computers is the Basic Input Output System more commonly called the BIOS.
The BIOS does one thing, it sends a “tick tock” command to the CMOS, which is a tiny semiconductor capable of launching a computer’s OS MBR or master boot record.
For the Big Bang model, the theory that Black Holes create Whole Holes and new universes, this process would be the BIOS or layer zero.
The four-easy pieces program is integral to the science collection called Embed with Electromagnetism currently an online exhibition.
